The Outcome
The requirements of MyMaskFit led to a more digital solution. By taking advantage of the concept of emerging distributed manufacturing (DM), an iconic hot topic recently year in UK, the project is aiming to develop a digital supply-chain marketplace (DSCM) that is digitally enabled, attractive to buyer and suppliers, and uses insight gained from other marketplace examples to address known barriers and issues. Through such dynamic and distributed supply chain, transforming customer feedback into designs and products can be achieved within days.
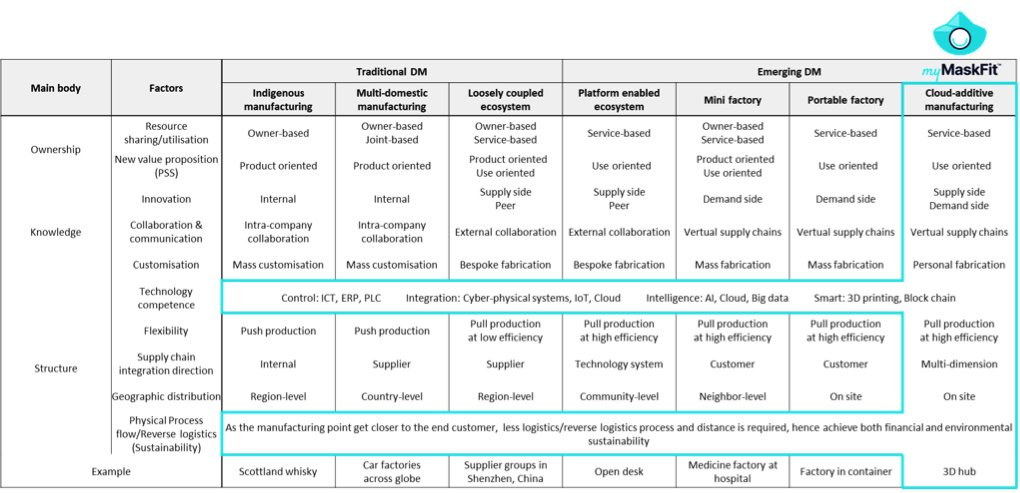
The WMG Supply Chain Research Group took a top down approach, and conducted a systematic literature review for the project and developed three theoretical frameworks: the first one explaining the 7 different archetypes of DM, from traditional to emerging models. The second framework illustrates the benefits of DM, from both company, consumer as well as social perspectives. The last one identifies enablers and barriers when applying DM. Other than that, managerial implications in developing DM strategy are suggested.
In the meantime, the WMG Accelerator Team took a bottom up approach, by leveraging their existed knowledge and lesson learned from UK Collaborative Commerce Marketplace (www.ukccm.co.uk), delivered detailed process flows where developed for the supply side and demand side of distributed manufacturing marketplaces as core templates to assess. In addition, a library of existing technology providers and marketplaces examples are listed for further collaborating and benchmarking.
MyMaskFits was then brought into the archetypes as the sample case (as shown in figure below) and proven that all factors meet the classification of cloud-additive manufacturing with a touch of the support of the platform (marketplace) to amplify the on-demand supply chain to a larger scale.